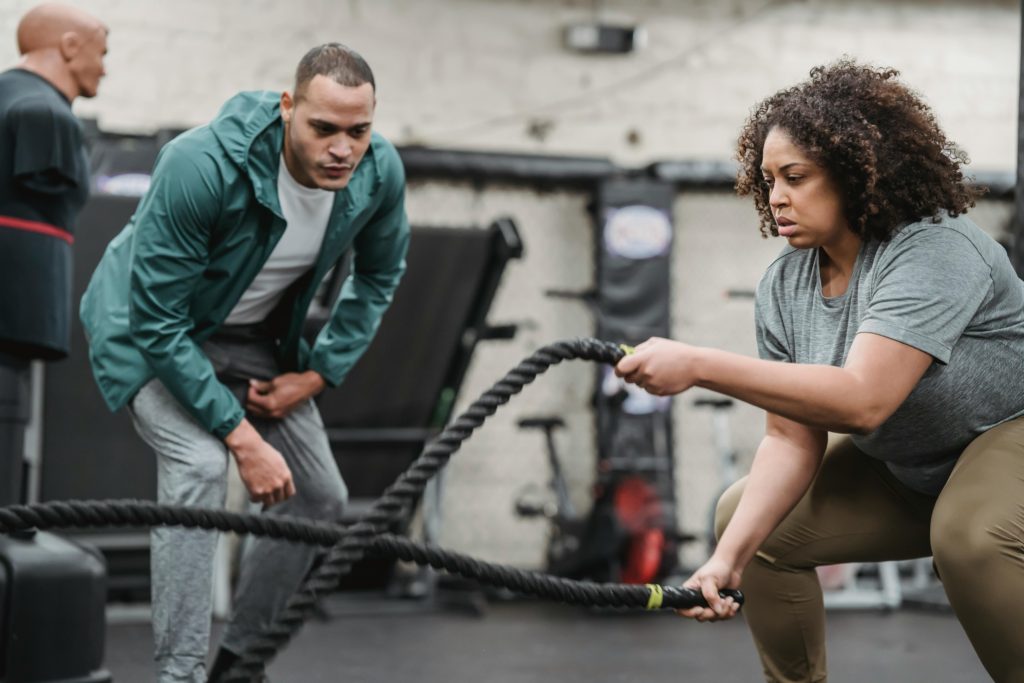
Welcome back to my blog! In the world of fitness, efficiency is key. For those with busy schedules, High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT) offers a powerful way to achieve impressive results in a short amount of time. Today, we’ll explore the benefits of HIIT workouts, why they are so effective, and provide some sample routines that you can do at home or at the gym.
What is HIIT?
High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT) involves short bursts of intense exercise alternated with low-intensity recovery periods. This method keeps your heart rate up and burns more fat in less time compared to traditional steady-state cardio. HIIT can be tailored to any fitness level and doesn’t require any special equipment, making it a versatile workout option.
The Benefits of HIIT
Efficiency
HIIT is renowned for its ability to deliver maximum benefits in minimal time. Studies have shown that just 20 minutes of HIIT can be as effective as 60 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise.
Calorie Burning
One of the main advantages of HIIT is its high calorie-burning potential. The intense bursts of activity elevate your metabolic rate, allowing you to burn more calories during and after the workout.
Improved Cardiovascular Health
HIIT has been proven to enhance cardiovascular health by improving blood pressure, reducing heart rate, and increasing overall cardiovascular endurance.
Muscle Retention
Unlike steady-state cardio, HIIT helps in retaining muscle mass while primarily focusing on burning fat. This is particularly beneficial for those looking to improve body composition without sacrificing muscle.
Flexibility and Accessibility
HIIT workouts can be performed anywhere – at home, in the gym, or even outdoors. They require little to no equipment, making them accessible to everyone, regardless of fitness level or location.
Sample HIIT Routines
Here are a few HIIT routines that you can incorporate into your fitness regimen. Each routine is designed to maximize your workout efficiency and can be adjusted based on your fitness level.
HIIT Routine 1: Bodyweight Blast (No Equipment Needed)
Warm-Up (5 minutes):
– Jog in place
– Arm circles
– Leg swings
Workout (20 minutes):
– 30 seconds of Jumping Jacks
– 10 seconds of Rest
– 30 seconds of Burpees
– 10 seconds of Rest
– 30 seconds of High Knees
– 10 seconds of Rest
– 30 seconds of Push-Ups
– 10 seconds of Rest
– 30 seconds of Mountain Climbers
– 10 seconds of Rest
– Repeat the circuit 3 times
Cool-Down (5 minutes):
– Stretching
– Deep breathing exercises
HIIT Routine 2: Gym Circuit
Warm-Up (5 minutes):
– Light cardio on a treadmill or stationary bike
Workout (20 minutes):
– 30 seconds of Kettlebell Swings
– 10 seconds of Rest
– 30 seconds of Box Jumps
– 10 seconds of Rest
– 30 seconds of Battle Ropes
– 10 seconds of Rest
– 30 seconds of Rowing Machine
– 10 seconds of Rest
– 30 seconds of Medicine Ball Slams
– 10 seconds of Rest
– Repeat the circuit 3 times
Cool-Down (5 minutes):
– Stretching
– Foam rolling
HIIT Routine 3: Quick Cardio Boost
Warm-Up (5 minutes):
– Dynamic stretches
– Light jogging
Workout (15 minutes):
– 1 minute of Sprinting
– 1 minute of Walking
– Repeat for 7 rounds
Cool-Down (5 minutes):
– Walking
– Stretching
Conclusion
High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT) is an incredibly effective way to maximize your workout results in minimal time. With its numerous benefits, including improved cardiovascular health, high calorie burn, and muscle retention, HIIT is a valuable addition to any fitness routine. Try incorporating these sample HIIT routines into your schedule and experience the transformative power of high-intensity interval training.
Stay active and keep pushing your limits!
Lexinton Forbes
Certified Personal Trainer
www.lexforbes.com
Sources:
- Journal of Sports Science & Medicine – HIIT Efficiency: https://www.jssm.org
- American College of Sports Medicine – HIIT and Calorie Burning: https://www.acsm.org
- Harvard Medical School – Cardiovascular Benefits of HIIT: https://www.health.harvard.edu
- National Institutes of Health – Muscle Retention with HIIT: https://www.nih.gov
- Mayo Clinic – Accessibility of HIIT Workouts: https://www.mayoclinic.org